This report briefly investigates into the standards of the Bluetooth phenomenon. Investigations into the workings of Bluetooth are given; an analysis of the potential new business creation is also explored. A close look at the security and safety issues relating to Bluetooth are examined.
Dr. George Carlo EMF Cell Phone Dangers Interview
Standards
Bluetooth supports, IEEE 802.11. Bluetooth is a de facto[1] standard for very low powered and short-range radio connections that would link your mobile phones and laptops, and allow them to access the Internet via hot spots[2].
The much-heralded wireless networking standard is seen as the solution to cutting the cables while increasing the connections of devices at home and work.
How Bluetooth Works?
Figure 1, Discovering a Bluetooth Device
Source: http://www.privateline.com/Bluetooth/Bray.pdf
Imagine two Bluetooth enabled devices; say for example a mobile phone and a laptop computer. The mobile phone is has a built-in modem. By configuring the dial up networking profile on the phone, it periodically scans to see if anyone wants to use it.
The user of the laptop runs an application which requires a Bluetooth dial-up network connection. To successfully use this application, the laptop knows it needs to establish a Blue-tooth connection to a device supporting the dial up networking profile.
First stage
The first stage is in establishing such a connection is finding out what Bluetooth enabled devices are in the area, so the laptop performs an inquiry to look for devices in the neighbourhood. To do this the laptop transmits a series of inquiry packets. Eventually the cell phone replies with a Frequency Hop Synchronisation (FHS) packet. The FHS packet contains all the information that the laptop needs to create a connection to the cell phone. It also contains the device class of the cell phone, which consists of major and minor parts.
Second Stage
The major device class tells the laptop that it has found a phone; the minor part tells the laptop that the type of phone is a cellular phone. This exchange of messages is illustrated in Figure 1.
In the same way, every Bluetooth-enabled device in the area which is scanning for inquiries will respond with an FHS packet, so the laptop accumulates a list of devices.
What happens next is up to the designer of the application.
Third Stage
The laptop could present the user with a list of all the devices it has found and let the user choose what to do next; but if it did that at this stage, all it could do was tell the user about the types of devices it has found. Instead of telling the user about the devices it has found, the application could automatically go on to the next stage and find out which devices in the area support the dial-up networking profile.
Global Perspective
The Bluetooth World Congress is in its 5th year. It is the world largest dedicated Bluetooth event. This year in particular focus in given to experience from the vertical markets as the implementation of technology increases.
Potential for New Business Creation
Ericsson has created a separate Bluetooth business[3], Mads Madsen a spokes person for Ericsson in Sweden said that the new company for which a name has not yet been decided has already begun operations. The company is based in Lund, Sweden. This is where Ericsson has it major Bluetooth research department. “The new company is an expansion of our existing business,” Madsen said. “We expect it to be a profitable business.”
Security
As Bluetooth’s role expands from small ad-hoc[4] networks comprised of a few wireless devices to an important part in online banking and mobile commerce, questions arise over its security. Is a Bluetooth network secure enough to transmit credit card numbers?
Not yet, seems to be the consensus. The Gartner Group, while saying Bluetooth “holds the promise of simplifying the life of the average mobile professional,” questions the technology’s security and is recommending a wait-and-see policy.
Two researchers from Lucent’s Bell Labs, a member of the Bluetooth Special Interest Group, recently discovered conversations could be easily bugged and encryption defeated, according to The New York Times. “I’m sure the NSA and FBI are salivating about building little Bluetooth receivers disguised as pencils, electrical outlets and phone cables,” wrote a member of a cryptography mailing list upon hearing the news.
For link encryption and authentication, Bluetooth uses a strong contemporary cipher algorithm available in the public domain called SAFER+[5].
Safety
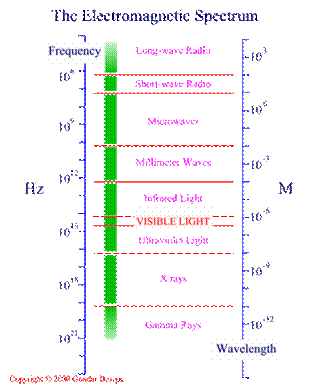
Figure 2, Source: http://www.purchon.com/physics/electromagnetic.htm
Bluetooth operate at 2.4 GHz[6]. 2.4 GHz is a microwave. Microwave oven also operate at this frequency 2.45 GHz. Please refer to Figure 1.
Microwaves have very short wavelengths; they are very easily absorbed by water. This is why they are used in microwave ovens. Water in your dinner absorbs the microwaves; the energy of the microwaves is converted into heat: this makes the water molecules vibrate faster. Fortunately, microwaves ovens contain the harmful microwaves contained inside a Faraday Cage[7].
There are concerns and people are even frightened that the radio waves coming out of their mobile phones are short enough to cook their brains.
There is no scientific proof that base stations[8] for mobile phones (power level of 20 Watts) have any damaging effects on living beings, even short exposures to high-power microwaves (like inside microwave ovens, in proximity of radar dishes, military airplanes and military electronic countermeasure systems, which all have power levels of about 500 Watts to 1 Giga Watt[9]) cause all tissue to heat up, which leads to the destructions of internal organs, and the whitening of the eye’s lens.
Consequences can range from blindness, organ failure, brain bleedings and death.
[1] A standard that comes to pass because everyone uses it, not because it was ordained as such.
[2] “hot spots” – areas where instant wireless broadband access to the Internet or a network is available to Bluetooth-enabled portable devices
[3] Ericsson creates separate Bluetooth business – News Bulletin by John Evers, Amsterdam correspondent for the IDG News Service, an InfoWorld affiliate. http://archive.infoworld.com/articles/hn/xml/00/11/22/001122hneric.xml
[4] Ad hoc networks are a new wireless networking paradigm for mobile hosts http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/zhou99securing.html
[5] SAFER+, generates 128-bit cipher keys from a 128-bit plain text input.
[6] http://www.privateline.com/Bluetooth/Bray.pdf
[7] Faraday Cage “The Faraday Cage Effect (named after its discoverer) means that the electric charge on a conductor sits on the outer surface of it. Therefore, no electrostatic field is present within the conductor” – http://www.rfsafe.com/research/rf_radiation/shielding_rf_hazards/faraday_cage.htm
[8] Base Stations are masts that mobile phone operators use to enable coverage of their network.
[9] Giga Watt is equivalent to 1024 Mega Watts.